CONSTITUTIONALITY CONTROL: easy to understand summary Cíntia Brunelli
233,991 views
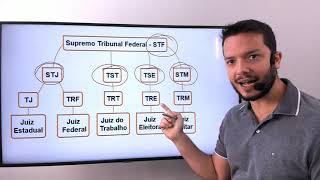
⚖️ FIRST STEPS IN LAW: the method for those who want to learn Law in a simple and objective way (without pulling your hair out because of boring classes or confusing books). ???? SIGN UP HERE: https://cintiabrunelli.com.br/direito ????⚖️ Read the book INTRODUCTION TO THE WORLD OF LAW and learn, in one afternoon, what Law students take 6 months to learn in college. ???? BUY HERE: https://cintiabrunelli.com.br/intro ???? Subscribe to the NOVATOS DO DIREITO channel: / @novatosdodireito ✅ VIDEO about Rules of FULL, CONTAINED AND LIMITED Effectiveness: • Rules of FULL, CONTAINED AND LIMITED effectiveness... ✅ VIDEO about DIRECT ACTION OF UNCONSTITUTIONALITY: • DIRECT ACTION OF UNCONSTITUTIONALITY... ???? EMAIL: [email protected] ===================================== What is Constitutionality Control? To understand this institute, I made an easy-to-understand summary of all the concepts we studied in the initial classes. Constitutionality control has two assumptions: the first of which is the hierarchy or supremacy of the constitution. No law can contradict the constitution. The second premise is the so-called principle of constitutional rigidity, which means that the law does not change the constitution. Our Constitution is rigid. Effects of the declaration of unconstitutionality: if a law is declared unconstitutional, the consequence is that it is considered null and void, which means that it is not valid. As a rule, the declaration of unconstitutionality produces retroactive effects (ex-tunc effect). The exception is the modulation of effects: if it is necessary to protect legal certainty and the social interest, the Supreme Federal Court (STF) can modulate the temporal effects, to give non-retroactive effects (ex-nunc). In the classification according to the types of unconstitutionality, we have unconstitutionality by ACTION, which is when an unconstitutional normative act was issued, and also unconstitutionality by OMISSION, which is the absence of a law regulating a constitutional norm of limited effectiveness. In cases of unconstitutionality by omission, there are basically two possible actions, called injunction and direct action of unconstitutionality by omission. In the classification according to the defect, we have material unconstitutionality, which is when the content of the normative act is contrary to the constitution, and formal unconstitutionality, which is when the normative act does not comply with the rules of the legislative process. Preventive control of constitutionality is what analyzes the draft of the normative act. This preventive control can be carried out by the three branches of government: executive, legislative and judiciary. The executive branch carries out preventive control by vetoing bills by the head of the executive branch. The legislative branch can exercise preventive control through an opinion from the committee on constitution and justice and also through the vote on the bill itself. The judiciary branch can carry out preventive control through a writ of mandamus that is filed by a parliamentarian who participates in the legislative process and wants to shelve the bill because it is unconstitutional. Repressive control of constitutionality: this is carried out after the promulgation of the normative act, and it is carried out solely by the Judiciary, and can be carried out in two ways: diffuse or concrete control or abstract or concentrated control. Diffuse or concrete control can be carried out in a diffuse manner, that is, by any judge or court (up to the judge of the first instance), and it is carried out based on specific cases. In diffuse control, the effects of the unconstitutionality ruling are inter partes: they are effective only between the parties to that specific case. In abstract or concentrated control, the normative act is analyzed in theory or abstractly and this control is concentrated because it is carried out by only two courts: STF, when the paradigm is the federal constitution, and TJ if the paradigm is the state constitution. In both diffuse control and concentrated control, it is necessary to observe the plenary reservation clause, which requires that the declaration of unconstitutionality be made by an absolute majority of the members of the plenary or special body (and not by a panel or by chamber). Among the actions of abstract or concentrated constitutional control, the most famous is the Direct Action of Unconstitutionality. Constitutional amendments can be declared unconstitutional when the content of the amendment tends to abolish a permanent clause or if the amendment does not comply with the rules of the legislative process (article 60 of the constitution). This video is for those who are in college or preparing for the Bar Exam (OAB) or public service exam. #CintiaBrunelli #ConstitutionalControl #ConstitutionalLaw 00:00 Leave your Like! 01:00 Not yet a subscriber? Subscribe :D 02:00 Special Links in the Description
336 x 280
Up Next
3 years ago
2 years ago
Streamed 6 hours ago
3 years ago
1 year ago
3 years ago
Streamed 1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
3 years ago
4 years ago
4 years ago
4 years ago
4 years ago
7 years ago
3 years ago
7 years ago
4 years ago
11 months ago
3 years ago
4 years ago
2 years ago
1 year ago
336 x 280